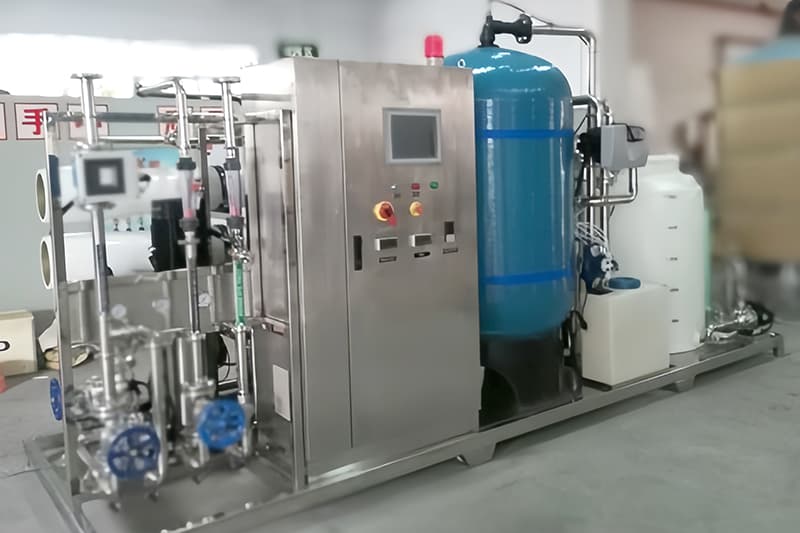
In industrial production, as the core equipment of thermal power, the stability of boiler operation directly affects the efficiency and safety of the entire production system. Boiler feed water treatment, as an important link to ensure the safe and efficient operation of boilers, cannot be ignored in its importance. This article will delve into various aspects of boiler feed water treatment, from basic concepts to practical operations, providing readers with a comprehensive and practical reference material.
What is boiler feed water treatment?
Boiler feed water refers to industrial water that has been chemically treated and transported from the deaerator to the boiler system through a feed water pump. In industrial fields such as thermal power generation, boiler feed water treatment is the fundamental link to ensure the safe and economical operation of boilers. The boiler feed water system usually consists of feed water tanks, boiler feed water pumps, water treatment equipment, condensate recovery devices, feed water pipelines, and valves.
Dissolved oxygen in water is the main cause of boiler pipeline corrosion, which can corrode the components of the boiler feed water system. The generated iron oxide enters the interior of the boiler, deposits or adheres to the boiler tube walls and heating surfaces, forming iron scale that is difficult to remove and has poor heat transfer performance. Corrosion can also cause pitting on the inner wall of the pipeline, increase the resistance coefficient, and in severe cases, may even lead to pipeline explosion accidents.
According to national regulations, steam boilers with an evaporation capacity greater than or equal to 2 tons/hour and hot water boilers with a water temperature greater than or equal to 95 ℃ must undergo deoxygenation treatment. This indicates that boiler feed water treatment is not only optional, but a mandatory safety measure required by laws and regulations.
Why is boiler feed water treatment so important?
The importance of boiler feed water treatment mainly lies in three aspects: preventing equipment scaling, avoiding metal corrosion, and ensuring steam quality.
Firstly, preventing scaling of thermal equipment is the primary task of boiler feed water treatment. If the inlet water quality of the boiler is poor, after a period of operation, solid attachments, namely scale, will form on the heating surface. The thermal conductivity of scale is extremely poor, only a few tens to hundreds of times that of steel. Research shows that the accumulation of 1 millimeter thick scale on the heating surface of low-pressure boilers can increase fuel consumption by 1.5% to 2.0%. Scaling not only significantly reduces thermal efficiency, but may also lead to an increase in boiler tube wall temperature, a decrease in metal strength, local deformation and bulging under pressure inside the tube, and even cause tube bursting accidents.
Secondly, avoiding metal corrosion is also crucial. The metal components of thermal equipment in power plants come into long-term contact with water, and if the water quality is not up to standard, it can cause serious corrosion. Corrosion not only shortens the service life of equipment and causes economic losses, but also allows corrosion products to enter water, exacerbating scaling on high heat load heating surfaces and forming a vicious cycle, which may quickly lead to pipe burst accidents.
Finally, ensuring steam quality is crucial for protecting downstream equipment. Poor water quality can prevent boilers from producing high-purity steam, and impurities carried in the steam can deposit in areas such as superheaters and turbines, forming salt deposits. Salt accumulation inside the superheater tube can cause overheating of the tube wall and even tube bursting; Salt accumulation inside the steam turbine can significantly reduce output power and efficiency, and in severe cases, even lead to emergency shutdown.
How does boiler feed water treatment work?
The complete workflow of a boiler feed water treatment system includes multiple stages, each with its specific functions and quality requirements.
Firstly, the intake and pretreatment of raw water. The raw water is usually taken from natural water sources such as Rivers and Lakes, and through pretreatment steps such as sedimentation and filtration, suspended solids and colloidal impurities are removed. The effectiveness of preprocessing directly affects the operational efficiency and lifespan of subsequent processing units.
The next stage is the fine processing stage, which may adopt various technologies based on the specific requirements of the raw water quality and boiler. Filtration and ultrafiltration are mainly used to remove fine suspended solids and colloids from water; Ion exchange softening removes hardness ions such as calcium and magnesium; Reverse osmosis and nanofiltration technologies are used for deep desalination.
Then comes the crucial step of deoxygenation treatment. Remove dissolved oxygen from water through methods such as thermal deoxygenation or vacuum deoxygenation. Modern boiler rooms often adopt new technologies such as analytical deoxygenation, separating the heating furnace from the reactor. The heated gas passes through the reactor for deoxygenation to ensure operational reliability and deoxygenation efficiency.
Finally, there is water quality regulation and distribution. The treated water may require adjusting the pH value or adding chemicals such as corrosion inhibitors. Qualified feed water is pumped into the boiler economizer through the feed water pump, and finally enters the steam drum to complete the entire processing flow.
Throughout the entire process, water quality monitoring is extremely important. Modern boiler feed water treatment systems are usually equipped with online monitoring equipment to monitor key indicators such as pH value, conductivity, and dissolved oxygen in real time. These monitoring data are not only used for process control, but also provide a basis for system optimization.
The design of boiler feed water treatment system needs to comprehensively consider factors such as boiler parameters, raw water quality, and operational requirements. The requirements for water quality vary greatly among boilers of different pressure levels, for example, high-pressure boilers require the salt content in the feed water to be less than 0.05 milligrams per kilogram. Therefore, choosing the appropriate combination of treatment processes is the key to ensuring the safe and economical operation of boilers.
What are the methods for boiler feed water treatment?
There are various methods for boiler feed water treatment, which can be divided into three categories based on principles: physical methods, chemical methods, and electrochemical methods.
Physical deoxygenation method
The physical method is mainly based on Henry’s law, which states that the solubility of a gas in water is proportional to its partial pressure. Common physical deoxygenation methods include thermal deoxygenation, vacuum deoxygenation, and analytical deoxygenation.
Thermal deoxygenation is one of the most commonly used methods, which can be divided into atmospheric thermal deoxygenation and jet deoxygenation. The principle is to heat the boiler feed water to the boiling point, reducing the solubility of oxygen in the water, allowing oxygen to continuously escape, and then discharge the oxygen and water vapor on the water surface together. This method can simultaneously remove multiple gases from water, including free carbon dioxide and nitrogen. The treated water does not increase the salt content, and the operation control is relatively simple, with stable and reliable operation.
Vacuum deoxygenation is a medium temperature deoxygenation technology, usually carried out within the range of 30-60 ℃. This method can utilize low-grade waste heat and has the advantages of good deoxygenation effect, stable operation, easy operation, and wide applicability. Compared to thermal deoxygenation, vacuum deoxygenation has more relaxed heating conditions and reduces the self consumption of steam in the boiler room.
Chemical treatment methods
Chemical methods remove dissolved oxygen from water through chemical reactions, converting it into stable metal compounds or other chemical compounds before entering the boiler. Commonly used methods include chemical deoxygenation and steel chip deoxygenation.
Sodium sulfite deoxygenation is a method of adding chemicals for deoxygenation inside the furnace. The higher the temperature, the shorter the reaction time, and the better the deoxygenation effect. This method has low investment, safety, and easy operation, but the dosage is difficult to accurately control, the deoxygenation effect is not stable enough, and it will increase the salt content of boiler water, resulting in an increase in pollutant discharge and heat waste.
Hydrazine deoxygenation is currently used as an auxiliary measure after thermal deoxygenation, which can completely remove residual oxygen in water without increasing the salt content of boiler water. However, due to the toxicity and volatility of hydrazine, it cannot be used for deoxygenation in drinking water boilers and domestic water boilers. Many boiler manufacturers are restricting or stopping the use of this method.
on exchange technology Ion exchange technology is one of the key processes in boiler feed water treatment. Ion exchange resin undergoes reversible exchange with ions in water through its functional groups, thereby purifying water quality. Cations such as calcium and magnesium in water are replaced by sodium or hydrogen ions on the resin, reducing the hardness of the water.
Comparison of Main Methods for Boiler Feed water Treatment
| Processing method | Working principle | Applicable conditions | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermal deoxygenation | By heating, the solubility of oxygen in water is reduced to allow it to escape | The water temperature needs to reach 104 ℃ | The deoxygenation effect is good and can remove other gases | High energy consumption, equipment needs to be installed at a high position |
| Vacuum deoxygenation | Reducing oxygen partial pressure under vacuum conditions to allow oxygen to escape | Water temperature 30-60 ℃ | Low energy consumption, suitable for low-temperature environments | Complex equipment requiring high-level installation |
| Chemical deoxygenation | Consuming oxygen in water through chemical reactions | Various water temperatures, requiring controlled dosage | Simple equipment, low investment | May increase salt content in water, requiring precise control |
| Ion exchange | Removal of calcium and magnesium ions through resin exchange | Regular resin regeneration required | Good treatment effect and high stability | High operating cost, requiring acid-base regeneration |
What are the components of a boiler feed water treatment system?
A complete boiler feed water treatment system consists of multiple key components, each responsible for different treatment tasks, working together to ensure that the final effluent quality meets the requirements of boiler feed water.
1. Pretreatment system
The pretreatment system is the first process, mainly targeting surface water raw water, with the aim of removing suspended solids, colloids, and organic matter from the water. Usually, coagulants (such as aluminum sulfate) are added to the raw water to condense impurities into larger particles, which are then precipitated and filtered. The main equipment includes pulse type, hydraulic acceleration type, and mechanical stirring type clarifiers, as well as siphon filters, valve free filters, and single and double flow mechanical filters.
2. Ion exchange system
The ion exchange system is the core component for removing hardness ions from water. Using natural or synthetic ion exchangers to convert hard salts such as calcium and magnesium into salts that are less prone to scaling, preventing the formation of calcium and magnesium hard scales on boiler tube walls. For high-pressure boilers, it is even required to remove all salt from the feed water, and desalination technology is needed in this case.
3. Membrane treatment system
The membrane treatment system includes advanced technologies such as ultrafiltration and reverse osmosis. Ultrafiltration passes through the ultrafiltration membrane in the membrane module, allowing solvents and low molecular solutes to pass through the membrane pores under pressure, while high molecular weight substances and colloidal particles are retained. Reverse osmosis uses a semi permeable membrane to separate dissolved salts in water, which is an efficient desalination method.
4. Deoxygenation system
The deoxygenation system is responsible for removing corrosive gases such as dissolved oxygen and carbon dioxide from water. Deaerators are usually installed at high positions to remove gas through heating or vacuum methods. The system also includes related equipment such as pipelines, pumps, valves, and control instruments.
5. Chemical dosing system
The chemical dosing system is used to add necessary chemical agents such as scale inhibitors, corrosion inhibitors, and pH regulators to the feed water. These chemicals further improve water quality and prevent scaling and corrosion inside the boiler.
What specific goals do boiler feed water treatment need to achieve?
The overall purpose of boiler feedwater treatment is to ensure that the water quality entering the boiler meets the specified standards through physical, chemical, and biological means, thereby ensuring the long-term stable operation of the boiler system. The specific goals include the following aspects:
Prevent scaling and sedimentation: By softening or desalination treatment, reduce the calcium and magnesium ion content in water, prevent scaling inside the boiler, and improve thermal efficiency. At the same time, physical methods such as filtration or precipitation are used to remove suspended particles in water, avoiding pipeline blockage and affecting boiler operation safety.
Control metal corrosion: By adding appropriate chemical agents, adjusting the pH value and dissolved oxygen content of the feed water, the corrosion rate of boiler metal materials can be slowed down. Dissolved oxygen is the main cause of boiler corrosion and must be effectively removed.
Improving thermal efficiency: Pure feedwater helps to enhance the heat exchange efficiency of boilers, ensure steam quality, and reduce energy consumption. The formation of scale will significantly reduce heat conduction efficiency and increase fuel consumption.
Extending equipment lifespan: Reasonable water treatment can reduce scale formation, prevent internal corrosion of boilers, and extend equipment lifespan. The lifespan of components such as pipelines, pumps, and valves in boiler systems is closely related to water quality.
Ensure safe operation: Good water treatment can prevent boiler failures caused by water quality issues and ensure the safe and stable operation of equipment. As a pressure vessel, the safety of boilers is directly related to the safety of personnel and equipment in the entire production system.
Concluzie
Boiler feed water treatment is a complex system engineering involving multiple disciplines and technologies. Its importance is not only reflected in improving boiler operating efficiency, but also directly related to equipment safety and service life. With the continuous advancement of technology, boiler feed water treatment technology is also constantly innovating, from early simple precipitation filtration to advanced technologies such as membrane separation and ion exchange today. In the future, boiler feed water treatment will pay more attention to system integration, intelligent control, and resource recovery, providing technical support for achieving green and sustainable development.
For boiler users, it is crucial to select appropriate treatment processes based on boiler parameters, raw water quality, and operating conditions, establish a scientific water quality monitoring system, and regularly maintain the system to ensure the effective operation of the boiler feed water treatment system. Only by fully mastering the principles, methods, and technologies of boiler feedwater treatment can the efficiency of the boiler system be fully utilized, and the operational goals of safety, economy, and environmental protection be achieved.
Obțineți o soluție astăzi!