Introduciton
Against the backdrop of increasingly scarce global water resources, teknologi desalinasi air laut has emerged as a key breakthrough in alleviating the freshwater crisis. This article delves into why seawater can be converted into drinking water, providing a detailed explanation of the core principles behind thermal desalination and membrane separation desalination.
How Seawater Desalination Technology Addresses the Global Drinking Water Crisis?
Approximately 71% of the Earth’s surface is covered by oceans, and seawater accounts for 96.5% of the world’s water resources. However, seawater contains large amounts of dissolved minerals such as sodium chloride, calcium carbonate, and magnesium sulfate, with sodium chloride alone accounting for approximately 77.7% of the total salt content in seawater, making it unsuitable for direct use as a drinking water source. Nevertheless, with the continuous innovation of seawater desalination technology, water is gradually emerging as a beacon of hope for addressing the global freshwater shortage crisis.
Why Can Seawater Be Desalinated into Drinking Water?
The salts and minerals in seawater are dissolved in water in ionic form, while water has a relatively low boiling point and exhibits significant physical differences from salts. Seawater desalination leverages these characteristics to separate salts from water through physical or chemical methods. Whether using thermal desalination or membrane separation desalination, the core principle is based on the physical and chemical differences between substances to achieve the goal of extracting pure freshwater from seawater.
How are Seawater Desalination Technologies: Principles, Advantages, and Challenges?
1. Thermal Desalination:
Thermal desalination has a long history. Its principle involves heating seawater to boil and evaporate it in an evaporator. The water vapor is then cooled and condensed into liquid freshwater in a condenser. Since the boiling points of salts and minerals are much higher than that of water, they remain behind during evaporation, thereby separating water from salts. Thermal desalination technologies such as Multi-Stage Flash (MSF) and Multi-Effect Distillation (MED) are widely applied in Gulf countries. For example, the Jebel Ali Desalination Plant in the United Arab Emirates uses MSF technology to produce up to 1.5 million cubic meters of freshwater daily. However, thermal desalination methods have high energy consumption, requiring approximately 20–40 kilowatt-hours of electricity per cubic meter of freshwater produced, and also have high equipment maintenance costs.
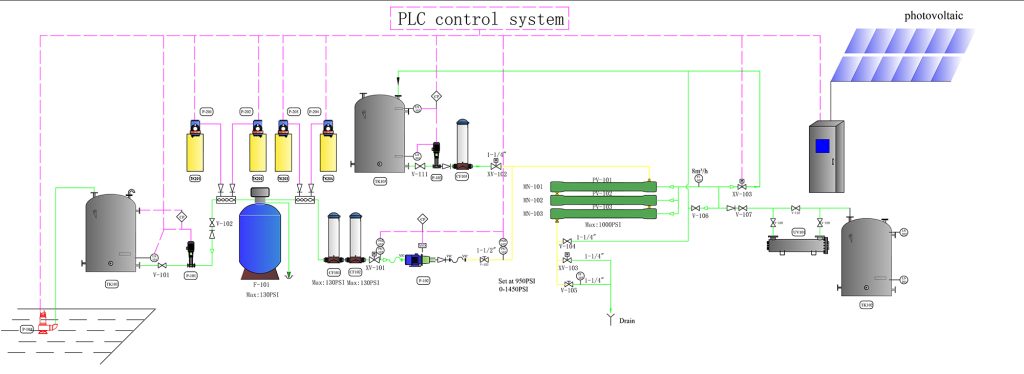
2. RO Membrane Separation Desalination Method:
Membrane separation desalination primarily relies on reverse osmosis (RO) membrane technology. RO membranes have extremely small pore sizes, approximately 0.0001 micrometers, effectively blocking salts, bacteria, viruses, and other substances in seawater while allowing only water molecules to pass through. Under pressure, seawater flows through the RO membrane, with high-salinity brine being discharged, while the freshwater filtered through the membrane is collected. This technology offers advantages such as simple operation, minimal land requirements, and relatively low energy consumption. For every 1 cubic meter of freshwater produced, energy consumption is approximately 3–5 kilowatt-hours. Currently, approximately 60% of new seawater desalination projects worldwide use reverse osmosis technology. However, membrane separation methods also face issues such as membrane fouling and the need for regular membrane element replacement, which increase operational costs.
| Desalination Method | Prinsip | Energy Consumption (kWh/m³) | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermal Desalination Method | Evaporation and Condensation | 20 – 40 | Mature technology, stable water quality | High energy consumption, large equipment, high costs |
| Membrane separation desalination method | Membrane filtration | 3 – 5 | Low energy consumption, compact footprint, flexible operation | Membranes prone to fouling, requiring regular replacement of membrane elements |
Social and Environmental Impacts of Seawater Desalination:
Seawater desalination not only addresses freshwater supply issues but also has multifaceted impacts on society and the environment. On the social front, it ensures water security for residents in water-scarce regions and promotes local economic development. On the environmental front, the discharge of brine from seawater desalination may affect marine ecosystems, such as altering the salinity and chemical composition of local marine areas, thereby impacting the living environment of marine organisms. Therefore, how to achieve green and sustainable development in seawater desalination has become an urgent issue for the industry to address. Currently, some regions have begun exploring comprehensive utilization technologies for brine, such as extracting valuable elements like magnesium and bromine to reduce negative environmental impacts.
Kesimpulan
Seawater desalination technology, with its unique principles and continuously innovative methods, provides an effective solution to the global water crisis. Despite current challenges such as high costs and environmental impacts, with advancements in technology and the widespread application of renewable energy, seawater desalination is poised to become an important freshwater supply source on par with traditional water sources in the future. From the traditional thermal decomposition desalination method to the modern membrane separation desalination technology, every breakthrough in seawater desalination technology is redefining the relationship between humanity and water resources, laying a solid foundation for the construction of a sustainable future water resource system.
Dapatkan Solusi Hari Ini!