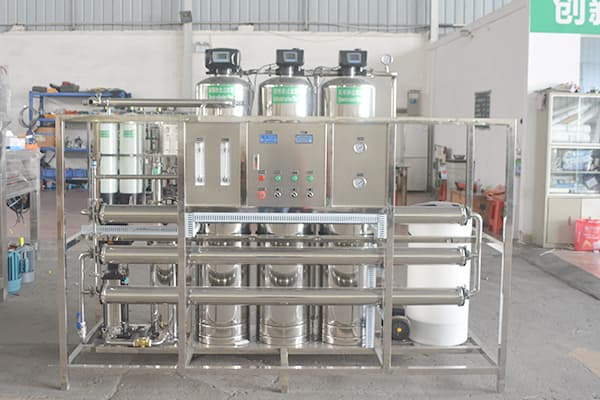
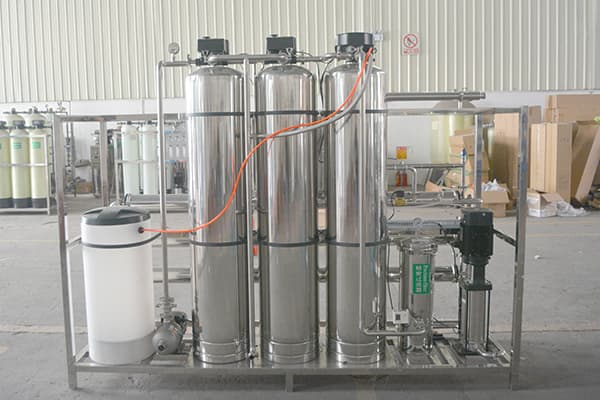
ระบบบำบัดน้ำป้อนหม้อไอน้ำ
KYsearo Boiler feed water treatment systems, specifically for steam generation requires high purity water, different depending on regions and scales. The feed water quality requirement varies depending on the manufacturer/generator, as well as the boiler model. Poor water quality or system design results in boiler life span shortening. The design of the water treatment system is a function of the water quality that varies dramatically depending on the water source and region.
The mature process for small to large scale boiler is RO+MB or RO+EDI, we can provide boiler feed water treatment systems for these water use:
- Marine boiler feed water system
- Power plant boiler water treatment
- Paper mill boiler water treatment system
- Textile mill boiler water treatment system
- Food industry boiler water supply system

Boiler Feed Water Treatment Process:
The main contaminants to remove are hardness, iron, silica, sodium and chlorides. The basic pretreatment process removes the suspended matter and particles before reverses osmosis and finally deionized in mixed bed or EDI device. RO pre-treatment commonly consists of coagulation, flocculation, clarification, sand filtration, ultrafiltration, etc. Essentially 100% of the suspended particles must be removed in the pre-treatment. RO removes approximately 98% of TDS in raw water.

Mixed bed or EDI is used at the last step to remove the residual ions, producing ultrapure water for feeding boiler. Resistivity of product water is usually over 10M3. the comparison between mixed bed and EDI is listed below.
| Principle | Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|
| Mixed bed Ion exchange | 1. Low input | |
| 2. Simpler pretreatment | 1. Chemical consuming | |
| 3. Stable product water quality | 2. Higher labor cost | |
| 4. Less water waste | ||
| EDI Ion exchange + electro deionization | 1. space saving | 1. High input |
| 2. higher water purity | 2. High requirement on pretreatment | |
| 3. non chemical consumption | 3. 10% water waste | |
| 4. automatic runningless labor cost | 4. Electricity consumption |
According to the information customer provided we help design the tailored water purification system for customers, taking consideration of invest, space, product quality, etc.
What is Boiler Feed Water Treatment System?
Boiler feed water therapy is essential for secure, efficient, and reputable steam generation in industrial and power facilities. Boilers transfer warm to water to create steam. Feed water top quality significantly affects system long life, efficiency, and safety. Untreated water has contaminations triggering scaling, deterioration, carryover, and fouling at high temperatures/pressures. These issues minimize thermal effectiveness, rise fuel usage, and can trigger equipment failing, expensive downtime, maintenance, and security dangers
Therapy shields assets like boiler tubes, drums, superheaters, and wind turbines by removing or neutralizing damaging impurities, maintaining optimum warm transfer, reducing energy losses, and prolonging devices life-span. It also ensures high-grade steam, essential for downstream processes like power generation and manufacturing, where polluted heavy steam can harm equipment and concession item high quality.
Overlooking therapy has substantial financial effects: performance loss from deposits, unintended downtime, premature equipment failure, enhanced gas costs, shed profits, and greater upkeep. Investing in robust therapy is therefore an economic need, not simply a governing one.
How Is Boiler Feed Water Working Process?
A typical system utilizes consecutive stages to eliminate pollutants. Setup depends on raw water high quality and boiler type/pressure
Usual phases:
- การเตรียมการก่อนการรักษา: Eliminates larger suspended solids, turbidity, sometimes decreases hardness/organics. Consists Of Screening, Clarification (coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation), Filtering (media, membrane) , Conditioning (ion exchange, lime), Triggered Carbon (chlorine, organics)
- Main Demineralization: Eliminates most dissolved salts/ions. Technologies: Reverse Osmosis (RO). (typically after softening/pretreatment, Electrodialysis Reversal (EDR).
- Sprucing Up (Advanced Demineralization): Accomplishes high pureness for medium/high-pressure boilers, getting rid of trace ions/gases. Technologies: Ion Exchange (multi-bed, mixed-bed for highest possible pureness), Electrodeionization (EDI/CEDI). (usually after RO .
- Deaeration: Eliminates dissolved oxygen/CO2 to avoid rust. Approaches: Thermal, Vacuum, Membrane layer Degasification.
- Chemical Conditioning: Includes chemicals to feed/boiler water for pH control, oxygen scavenging, conditioning continuing to be solids.
Dealt with water feeds the boiler. Condensate return is gathered, brightened, and combined with make-up water to minimize fresh water need.
Real systems differ based upon needs and raw water.
What Technologies Are Used For Boiler Feed Water Treatment System?
Equipments make use of physical, chemical, and thermal technologies, usually integrated.
- Information and Filtration: Preliminary actions for put on hold solids/turbidity. Coagulation/Flocculation/Sedimentation usage chemicals to clump particles for elimination. Media Purification utilizes granular beds. Membrane Layer Purification (MF, UF) makes use of pores to eliminate bits, bacteria, infections; UF eliminates colloidal silica, utilized before RO.
- Softening (Ion Exchange): Salt softening eliminates hardness (Ca, Mg) by exchanging them for salt on material. Resin restored with brine.
- Reverse Osmosis (RO): Membrane procedure removing ~ 99% of dissolved salts, silica, organics, bacteria under high stress. Pretreatment prevents fouling.
- Electrodialysis Turnaround (EDR): Electrochemical procedure utilizing membranes and electric field to remove salts. Polarity turnaround minimizes scaling. Takes care of higher suspended solids than RO.
- Demineralization (Ion Exchange): For high purity, gets rid of nearly all ions. Two-bed/Multi-bed systems utilize different cation/anion beds. Mixed-bed systems integrate materials for greatest pureness.
- Electrodeionization (EDI/CEDI): Incorporates resins, membranes, electric field. Gets rid of trace ions constantly without chemical regeneration. Sprucing up step after RO.
- Deaeration (Thermal, Vacuum Cleaner, Membrane Layer): Thermal heats water to strip gases. Vacuum reduces pressure. Membrane uses gas-permeable membranes.
- Chemical Conditioning: Injects chemicals for corrosion control, scale avoidance, sludge monitoring. Oxygen Scavengers remove DO. pH Control (caustic, amines) preserves pH. Range Inhibitors/Dispersants protect against hard scale.
Technology option depends upon raw water, needed pureness (boiler stress), and business economics.
How we design Boiler Feed Water Treatment System?
Design is complex, taking into consideration boiler type/pressure, system scale, and raw water quality.
- Boiler Type/Pressure: The majority of considerable factor for pureness needs. Low-pressure (<15 bar) tolerates more impurities, often needs only softened water/basic chemicals. Medium-pressure (15-60 bar) needs higher purity, often RO after softening. High-pressure (>< 15 bar) endures even more pollutants, typically needs just softened water/basic chemicals. Medium-pressure( 15-60 bar) needs greater pureness, commonly RO after softening. High-pressure( > 60 bar) needs extremely high purity( reduced solids, silica, gases), calling for multi-stage therapy (RO, polishing with mixed-bed IX or EDI ), efficient deaeration. Silica elimination is essential at high pressures. Stainless-steel boilers need extremely reduced conductivity water.
- System Size/Application: Scale( little commercial vs. big energy) influences capacity/redundancy. Huge plants need constant, trustworthy systems. Application (process home heating, power, pharma) determines pureness; turbine vapor needs high purity.
- Raw Water Quality: Pollutant profile dictates innovation series. High solids need clarification/filtration. High firmness needs softening.High TDS/silica requirement RO/EDR. High gases require deaeration.High organics might require turned on carbon/AOPs.
- Economic Considerations: CAPEX and OPEX are vital. Complicated systems set you back a lot more. Lifecycle price analysis (LCCA) contrasts options [61] Power, chemicals, membrane/resin substitute, garbage disposal are OPEX factors.
- Regulatory Conformity: Feed water must fulfill requirements (ASME, ABMA, VGB, EN) and ecological regulations.Requirement set restrictions by boiler type/pressure.
- Space/Footprint: Available area affects modern technology choice (e.g., IX demands a lot more room than RO/EDI).
- Waste Generation: Technologies produce different waste (brine, spent chemicals). Disposal costs/regulations influence selection. Fads aim for absolutely no liquid discharge (ZLD).
Layout equilibriums called for purity (central heating boiler type/pressure), raw water characteristics, and economic/environmental elements.
Monitoring, Control, and Efficiency Assessment
Tracking and control guarantee constant water quality and efficient operation. Real-time monitoring finds variances and troubles early.
Trick criteria kept track of:
- Conductivity: Total dissolved ions; indicates impurity degrees.Kept track of at phases to assess performance. Cation conductivity steps harsh anions in high-purity systems.
- pH: Acidity/alkalinity; crucial for deterioration control. Monitored in raw, dealt with, central heating boiler water.
- Dissolved Oxygen (DO): Crucial for rust control. Need to be extremely reduced (< 5 ppb) in feed water for high-pressure boilers. On the internet analyzers check deaerator performance.
- Silica: Vital in high-pressure systems to prevent scale/turbine deposits. On the internet analyzers make certain restrictions are satisfied.
- Hardness: Checked after softening. Online analyzers offer continuous check.
- Sodium: Kept track of in high-purity systems after IX/EDI.
- Alkalinity: Kept an eye on to control lathering, carryover, caustic corrosion.
- Turbidity: Suspended solids; displays filtration/clarification and secures membranes.
Monitoring/Control Techniques:
- Online Analyzers: Constant, real-time dimensions (pH, conductivity, DO, silica, etc). Use advanced sensing units.
- Get Hold Of Sampling/Lab Analysis: Regular checks to confirm on-line information and evaluate non-continuous parameters.
- Control Systems: PLCs/DCS automate procedure based upon online signals (pumps, valves, dosing, regrowth).
- Data Acquisition/Management: Collects, shops, examines information for fads, performance, issues. Cloud/IoT made use of for real-time surveillance, analytics, remote access.
- Automated Chemical Dosing: Integrates online monitoring to manage chemical shot based on real-time data.
Performance reviewed against feed water specifications (boiler maker, standards like ASME). KPIs include: cured water top quality consistency, pollutant elimination efficiency, chemical/energy use, regrowth frequency, membrane layer efficiency, blowdown price. Data help anticipating maintenance and fixing. AI can analyze information for anomaly detection and failure forecast.
Operational Difficulties, Troubleshooting, and Advanced/Emerging Solutions
Difficulties influence water top quality, performance, expenses, and central heating boiler reliability. Fixing and advanced options maximize efficiency.
Usual problems:
- Membrane Fouling/Scaling: RO/EDI membranes fouled by solids, organics, microorganisms, scaled by salts if pretreatment is bad. Decreases circulation, raises stress.
- Troubleshooting: * Display stress, circulation, rejection. Use cleaning-in-place (CIP).
- Advanced Solutions: * Fouling-resistant membranes, boosted spacers, advanced pretreatment (UF, NF).
- Ion Exchange Material Exhaustion/Fouling: Resins have finite capacity, need regrowth. Fouled by organics, iron, chlorine, lowering capability.
- Troubleshooting: * Display conductivity/silica leakage. Check regeneration. Evaluate resin.
- Advanced Solutions: * CEDI gets rid of chemical regeneration. Enhanced materials, enhanced regrowth.
- Deaerator Performance: Inefficient elimination leaves high DO/CO2, causing rust. Problems: not enough heating, stress control, harmed internals.
- Troubleshooting: * Monitor DO, temperature level, vapor flow/pressure. Examine internals.
- Advanced Solutions: * Membrane degasification for extremely reduced DO, improved deaerator styles.
- Sludge/Sediment: Inadequate solids removal causes accumulation in clarifiers, filters, boiler.
- Troubleshooting: * Screen turbidity/solids. Inspect filter backwash. Display boiler blowdown.
- Advanced Solutions: * Advanced purification (VSEP), enhanced clarifiers, automated blowdown.
- Corrosion: Due to residual gases, low pH, chlorides.
- Troubleshooting: * Monitor pH, DO, chlorides. Check elements.
- Advanced Solutions: * Real-time electrochemical deterioration tracking, corrosion-resistant products, maximized chemical application
- Carryover: Brought on by high solids/alkalinity in boiler water or improper operation.
- Troubleshooting: * Screen vapor pureness (conductivity, salt, silica). Inspect central heating boiler water chemistry. Testimonial procedure.
- Advanced Solutions: * Boosted central heating boiler internals, progressed central heating boiler water treatment, stricter feed water control.
Advanced/Emerging Solutions: Driven by sustainability, purity needs, expense optimization.
- Integrated Membrane Layer Equipments: Incorporating UF+RO+EDI enhances elimination, decreases chemicals/footprint
- No Liquid Discharge (ZLD): Recovers/reuses mostly all water, reducing waste. Uses MD, crystallizers.
- Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs): Utilize oxidants (ozone, UV) to break down complicated organics/micropollutants.
- Electrochemical Therapy: Past EDI, discovers removing details pollutants or controlling deterioration.
- Digitalization/AI: Sensing Units, IoT, AI/ML for real-time tracking, predictive maintenance, optimization, automation. AI evaluates information for patterns, forecasts, dosing optimization.
- Unique Adsorbent Products: New materials careful for silica, boron, and so on
- Energy Recovery: Utilizing waste warmth (e.g., from nuclear power plant) for procedures like FO/MD enhances system energy efficiency.
Contrarian Ideas/Speculation:
- Decentralized Therapy: Smaller, modular devices near factor of use for adaptability, redundancy, reduced piping? (Speculation).
- Organic Pretreatment: Engineered biological processes for lasting removal of organics/inorganics from challenging sources? (Conjecture).
- Direct Vapor from Lower Top Quality Water: Could progressed materials/design allow straight heavy steam generation from slightly greater pollutant water, decreasing exterior treatment complexity? Needs getting over scaling/corrosion obstacles. (High Conjecture).
- Contamination Change: Create modern technologies to change damaging contaminations right into benign/valuable substances as opposed to removing them? (High Conjecture).
Resolving obstacles needs surveillance, troubleshooting, and embracing advanced remedies. Pattern is in the direction of incorporated, automated, lasting systems lessening chemicals, waste, power, while ensuring reliability and purity. LCCA is essential for evaluating innovative remedies.
Purposes of Feed Water Therapy
The major goal is to prepare raw water to fulfill quality specifications for safe, reliable central heating boiler operation by removing or controlling pollutants. Key goals consist of:
- Stopping Scale: Impurities like calcium, magnesium, and silica develop hard range on warm surface areas, minimizing efficiency, creating overheating, and potential tube tear. Eliminating hardness and silica is vital.
- Managing Rust: Liquified gases (oxygen, CARBON DIOXIDE) trigger matching and basic deterioration, deteriorating devices. Deaeration and pH control are vital.Iron oxides likewise add.
- Reducing Carryover: Boiler water contaminations (solids, alkalinity) entrained in heavy steam contaminate downstream equipment (turbines, warmth exchangers), creating deposits, corrosion, and water hammer. Managing central heating boiler water chemistry (TDS, alkalinity) and optimizing operation minimize carryover.
- Ensuring Steam Pureness: High-purity heavy steam is essential for sensitive tools like turbines. Strict control of liquified solids, silica, sodium, and TOC in feed and central heating boiler water is required.
- Reducing Sludge: Put on hold solids and precipitates form sludge, lowering warm transfer and creating under-deposit corrosion. Filtering and blowdown manage sludge.
- Maintaining Ideal Chemistry: Treatment preserves central heating boiler water pH, alkalinity, and chemical concentrations within limitations for scale and corrosion security.
- Avoiding Failings: Addressing scaling, deterioration, and carryover reduces unexpected closures, damage, and safety dangers, making sure reputable procedure.
These goals collectively maximize boiler life-span, boost effectiveness, decrease upkeep, and make certain security and dependability.
Characterization of Raw Water Sources
Evaluating the raw water resource is the initial step in developing therapy. Quality varies by source (metropolitan, well, surface area), each providing distinct pollutants. Analysis identifies and evaluates crucial parameters to select modern technologies. Vital parameters:
- Hardness: Calcium and magnesium; major range cause
- Alkalinity: Bicarbonates, carbonates, hydroxides; can create frothing, carryover, caustic corrosion
- pH: Acidity/alkalinity; influences deterioration prices
- Conductivity: Overall dissolved ions (TDS); suggests scaling/corrosion possible
- Silica: Forms hard range, troublesome in high-pressure central heating boilers
- Liquified Gases: Oxygen and carbon dioxide; very destructive
- Overall Organic Carbon (TOC): Fouls materials, contributes to rust, frothing, carryover
- Suspended Solids: Undissolved particles; reason disintegration, sludge, fouling
- Iron and Manganese: Create fouling and deposits
- Chlorine/Chloramines: Damages resins and membranes
Understanding the pollutant account and irregularity is essential for a durable system. Extensive evaluation and treatability studies predict pollutant actions and determine therapy actions. On-line monitoring supplies real-time data.
Key Pollutants and Their Impact
Pollutants in raw water injury central heating boiler components, performance, and steam high quality. Understanding their effect guides therapy:
- Firmness (Calcium, Magnesium): Primary range formers. Speed up when heated up, forming shielding deposits on tubes, decreasing warmth transfer, boosting fuel use, triggering getting too hot and tear. Can restrict circulation.
- Liquified Solids (TDS): High levels in boiler water boost conductivity, triggering foaming and carryover. Carryover pollutes heavy steam, damaging downstream tools. Controlled by blowdown; treatment reduces blowdown demands.
- Silica: Problematic in high-pressure boilers. Kinds hard, protecting scale. Can evaporate with heavy steam and deposit on wind turbine blades, creating discrepancy.
- Liquified Gases (Oxygen, CARBON DIOXIDE): Oxygen triggers matching corrosion. CO2 types carbonic acid, causing basic deterioration in condensate/boiler [6] Have to be gotten rid of.
- Alkalinity: High degrees create foaming/carryover. High hydroxide can create caustic corrosion under down payments.
- Put On Hold Solids (Turbidity): Cause erosion, sludge, down payments, minimizing warm transfer and causing under-deposit deterioration. Foul membranes/resins.
- Iron and Manganese: Cause discoloration and deposits; foul treatment tools.
- Chlorides: Contribute to corrosion, especially anxiety breaking in stainless-steel.
Pollutant visibility and focus determine therapy system complexity and cost. Reliable removal/control is fundamental for reliable, efficient boiler procedure.
Get The Solution Today!
Related Products