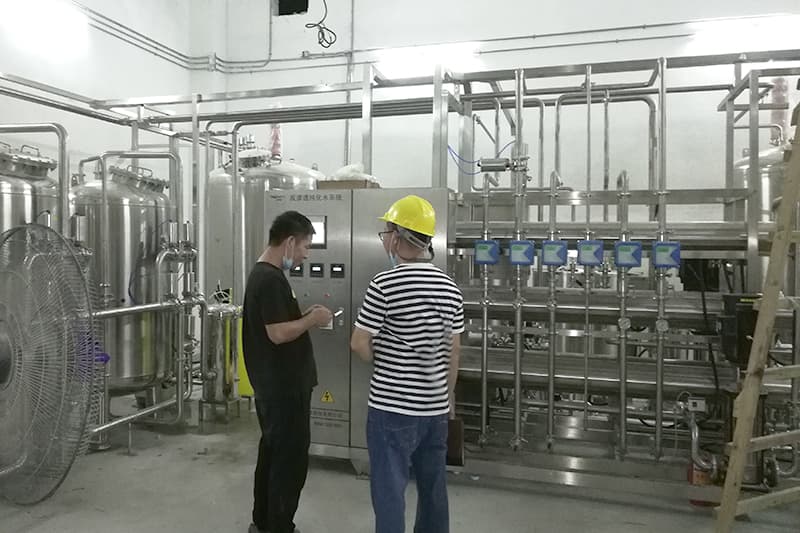
Reverse osmosis water purification plants are presently the mainstream purification tools in the water treatment industry. Their core modern technology includes filtering system water via a reverse osmosis semi-permeable membrane. Especially, the system uses a high-pressure pump to raise the pressure of the source water, developing osmotic stress that compels it via the semi-permeable membrane. This membrane has pore sizes as tiny as 0.0001 microns, precisely preserving impurities such as hefty metals, bacteria, infections, and organic compounds, while permitting only water molecules to travel through. This process creates highly detoxified water.
Highly, the essential difference in between reverse osmosis purification plants and standard filtration systems hinges on their “energetic separation” system: while standard filters count exclusively on physical interception to detoxify water, reverse osmosis utilizes stress differentials to efficiently different solutes from solvents, attaining filtration precision surpassing 99%. As an example, when treating hard tap water, reverse osmosis membrane layers properly remove calcium and magnesium ions, decreasing water solidity and avoiding range formation.
What Are the Advantages of Reverse Osmosis Water Purification Plant?
1.Reverse osmosis technology remove harmful substances from water:
- Microbial Level: Filters germs like E. coli and Salmonella (elimination price ≥ 99.9%), as well as infections (e.g., hepatitis B, influenza);.
- Chemical Contaminants: Adsorbs heavy steel ions (lead, cadmium, chromium), natural pesticide deposits (e.g., DDT), residual chlorine, and so on;.
- Liquified impurities: Reduces complete dissolved solids (TDS) to achieve direct drinking requirements (TDS < 50mg/L).
2. Eco-friendly and Energy Efficient, Aligned with Sustainability Concepts:
Unlike chemical filtration or electrodialysis, reverse osmosis systems require no chemical additives, preventing secondary contamination; Functional power intake mainly originates from the high-pressure pump, generally ranging in between 30-50W, with day-to-day power use under 0.5 kWh, conference nationwide Course 1 power performance criteria. Based on a typical home day-to-day water intake of 10L, annual electricity usage is around 150 kWh, attaining over 70% energy financial savings compared to typical boiling techniques.
3. High Scenario Adaptability and User-Friendly Operation:
- Residential Scenarios : Countertop designs (e.g., under-sink devices) occupy only 0.1 m two and link straight to municipal water lines for instant filtering and drinking.
- Industrial Situations : Food service establishments and cafes can make use of business models with 50-100 L/h production ability to guarantee beverage high quality.
- Industrial Applications : High-purity water (18.2 MΩ · centimeters) is generated utilizing reverse osmosis + EDI (electrodeionization) systems in electronics factories, pharmaceutical plants, and various other markets with strict water high quality needs.
Are Reverse Osmosis Water purification plant Suitable for All Circumstances?
Despite their substantial advantages, reverse osmosis systems encounter limitations in application because of:.
1. Cost and maintenance
- Equipment Cost: Residential systems typical $300– 800, while commercial systems can reach tens of thousands;.
- Maintenance prices: RO membranes typically last 2-3 years, with replacement expenses around 100-200 USD dollars per cycle. Combined with periodic substitute of pre-filters (PP cotton, triggered carbon), annual upkeep costs typical 300-800 RMB. This poses considerable financial stress for local business or country households with minimal spending plans.
2.Water source application: Concentrate discharge problem .
The “wastewater ratio” is an essential metric for reverse osmosis systems: standard models run at 1:3, while newer water-saving models can enhance this to 1:1. In arid regions like Northwest China or water-scarce environments, high wastewater ratios may worsen water usage problems. Prioritize water-saving certified products.
3.Setup and Technical Requirements
Equipment setup calls for specialist technicians for pipe links and water pressure testing (optimal pressure: 0.4-0.8 MPa). If raw water stress exceeds 1MPa, mount a pressure-reducing shutoff. For bad water quality (e.g., high sediment web content), add a pre-filter to avoid membrane layer component premature failing.
Why Choose Reverse Osmosis Technology for Safe Drinking Water?
Ultimate Purification Effectiveness: Reverse osmosis membranes eliminate over 99% of harmful compounds like heavy steels, pesticide deposits, and infections, making them excellent for areas with severe water contamination. Unlike traditional filtration, its outcome is safe for straight intake, completely removing waterborne condition threats.
Source Performance: Operation requires no home heating, accomplishing significant power cost savings with ambient-temperature filtering. Modern designs maximize wastewater ratios to 2:1 and even 1:1. Incorporated with wastewater reusing innovations (e.g., irrigation, cleaning reuse), this considerably lowers water waste.
Long-Term Cost-Effectiveness: RO membrane life expectancy gets to 2-3 years, while pre-filter PP cotton and turned on carbon cartridges call for substitute every 6-12 months. Modular style maintains maintenance prices convenient.

How to Optimize the Operational Efficiency of Reverse Osmosis Water Purification Plant?
1. Scientific Maintenance of Filter Cartridges Replace
RO membranes every 2-3 years. Replace pre-filters every 6-12 months based on water quality to prevent membrane pressure damage caused by clogging. During prolonged shutdowns, perform low-pressure flushing of membrane modules every 48 hours to prevent bacterial growth.
2. Operational Parameter Monitoring
Water pressure must be stabilized between 0.2-0.4 MPa. Low pressure will trigger shutdown protection. Regularly check TDS values and output flow rate; abnormal fluctuations indicate the need to clean the membrane surface or replace filter cartridges.
3. System Upgrade Strategy
In areas with high water hardness (>450 ppm), add softening pretreatment. Commercial sites may opt for zero-stagnant-water technology models to prevent first-cup water exceedances. IoT models support mobile monitoring of filter life and water quality reports.
Phần kết luận
As a core tool in modern-day water treatment, reverse osmosis water purification plant provide reliable water quality assurance for household, industrial, and industrial setups with their high-efficiency filtration capabilities. Nonetheless, customers must scientifically pick designs based on water high quality problems, budget restrictions, and application scenarios while prioritizing routine upkeep to make best use of device efficiency. With continuous technical improvements, future RO systems will achieve greater advancements in power performance, ecological sustainability, and smart capability, adding even more possibilities to international water purification efforts.
Get A Quote Today!