كيسارو
Industrial Reverse Osmosis Systems Manufacturer
Industrial & Commercial Reverse Osmosis (RO) Systems
As a manufacturer of industrial reverse osmosis systems, KYsearo offers a one-stop service from system design to operation and maintenance: This includes customising reverse osmosis system solutions tailored to customer needs (adapted to water quality, water production volume, and industry characteristics), as well as the research, development, manufacturing, and quality control of main componentst (spiral-wound membrane modules, high-pressure pumps, and intelligent control systems); providing on-site professional installation, commissioning, and operator training to ensure stable system operation; We also offer regular maintenance services (such as membrane cleaning, parameter monitoring, and microbial control) and establish a rapid response mechanism to promptly address operational issues.
Why Choose KYsearo?
KYsearo is an environmentally friendly high-tech enterprise integrating water treatment equipment and accessories. We offer a wide range of water treatment equipment, including reverse osmosis systems, ultrafiltration systems, EDI (Electrodeionisation) systems, نظام تحلية مياه البحرs, as well as various accessories such as mechanical filters and activated carbon filters. These products are widely applied in industries such as electronics, electroplating, power plants, and pharmaceuticals. The company’s products follow the trends of well-known European and American brands, ensuring excellent quality and performance.
Solution Design Services: KYsearo has a professional R&D team that designs customised water treatment solutions based on the client’s industry, water quality conditions, and water usage requirements.
Equipment Selection Services: Among various equipment types such as seawater desalination, brackish water desalination, reverse osmosis pure water, softened water, ultrafiltration, and EDI ultra-pure water systems, we precisely select the most suitable equipment for our clients.
Construction and Installation Services: We dispatch experienced technical personnel to the site to install and commission equipment in accordance with design specifications and industry standards, ensuring secure equipment installation, tight pipe connections, and safe and reliable electrical systems, enabling the equipment to operate smoothly.
After-sales technical support: We offer 7×24-hour technical support, providing solutions within 30 minutes of equipment failure and resolving issues within 24 hours.
احصل على الحل الآن
What is Industrial Reverse Osmosis Systems?
Industrial Reverse Osmosis (RO) is a membrane-based process separating a solvent, normally water, from liquified solutes by applying pressure exceeding natural osmotic pressure. Osmosis naturally moves solvent from reduced to high solute concentration; RO reverses this flow, forcing solvent from high to reduced concentration, leaving solutes behind.
Splitting up primarily follows the solution-diffusion version : solvent liquifies into the membrane layer, diffuses across, and desorbs. Dimension exemption (approx. 1 nm pores) and charge repulsion (especially for ions).
RO advancement progressed substantially in the 1960s with asymmetric cellulose acetate membranes by Loeb and Sourirajan. Modern systems use thin-film composite (TFC) polyamide membrane layers with high salt rejection (> 99.5%).
Contrasted to thermal methods, RO operates at ambient temperature without stage adjustments, ideal for heat-sensitive materials and generally reduced energy. RO creates high-quality water, often satisfying laboratory criteria.
Key elements consist of RO membrane components, a high-pressure pump, and pre-filtration. The rejected water stream is called concentrate or brine.
RO differs from Nanofiltration (NF), which has larger pores (0.001-0.01 µm) and primarily denies multivalent ions. Diafiltration utilizes UF/NF membrane layers to eliminate low molecular weight solutes from macromolecules.
Microbial regrowth can occur on the penetrate side if system layout, tracking, and maintenance are insufficient.
What are the technologies of industrial reverse osmosis systems?
RO is a leading modern technology yet exists together with others.
Comparative Technologies: RO offers high effectiveness, low energy vs. thermal, minimal environmental impact, but requires pre-treatment for fouling/scaling.
- NF: Larger pores, gets rid of multivalent ions/organics.
- UF/MF: Eliminate put on hold solids, germs, viruses; typically RO pre-treatment.
- EDR: Electrochemical, moves ions; for brackish water/selective removal. Crossbreed RO-EDR exists.
- FO: Utilizes draw option for osmotic slope; much less power for water transport however needs draw remedy splitting up; helpful for concentrated/fouling feedwaters.
- MD: Thermal, hydrophobic membrane passes vapor; for high salinity/challenging feedwaters, uses low-grade warm.
- Thermal Desalination (MSF, MED): Energy-intensive, take care of high salinity. Crossbreed RO-thermal systems explored.
Hybrid RO systems combine processes (RO-EDR, RO-FO, RO-NF) for boosted separation, quality, and efficiency.
What are the applications of industrial reverse osmosis systems?
Industrial RO systems are made use of across varied sectors such as desalination, wastewater treatment, food/beverage, and pharmaceuticals. Strategic goals consist of accomplishing high-purity water, recovering sources, and concentrating remedies.
Trick calculated motorists:
- Environmental Rules: Fulfilling rigorous laws like RoHS is essential. Decreasing wastewater discharge enhances public health and wellness and compliance.
- Water Deficiency: Decreasing reliance on freshwater through reuse and recycling improves resilience.
- Expense Decrease: Decreasing prices for fresh water purchase, therapy, and wastewater disposal enhances competition.
- Water Circularity: Decentralized circularity supplies substantial water savings (50-75% possibility, 85-90% with complete technique).
- Product Effectiveness: Recovering valuable materials from wastewater sustains a circular economic climate.
- Sustainability: RO aligns with corporate sustainability objectives and gets ready for future guidelines.
Industry-specific vehicle drivers:
- Light Industries: Moving from linear water use to round designs with RO for recovery.
- Production: Dealing with effluent including contaminants like heavy steels to meet discharge high quality.
- E&E Industry: Interior (policy, resources) and external (laws, rates) elements drive water reuse using RO.
Governing structures (e.g., EU directives) and rising raw material costs additionally incentivize RO adoption. Water savings convert to financial advantages .
Effective implementation relies on inner variables (plan, sources, structure, employee commitment). and external events highlighting durability needs. Insight in policy stresses resource administration.
Particular applications include salt water desalination, wastewater recuperation, ZLD, alcohol consumption water softening , and point-of-use therapy.
How is industrial ro system style, architecture, and scaling?
Industrial RO system layout involves pre-treatment, RO separation, and post-treatment.
المعالجة المسبقة: Crucial for membrane layer longevity and efficiency, preventing fouling, scaling, chemical strike, and damages. A multi-barrier strategy is tailored to feed water. Steps include: Mesh filtration (> 5µm), sanitation, coagulation/flocculation. antiscalant application, chlorine/organics removal (turned on carbon, chemicals, oxidation)., final cartridge filters (1-50µm). Advanced alternatives like MF/UF remove smaller bits. Information may be required for high turbidity. pH modification assists avoid range.] Biofouling control needs integrated strategies.
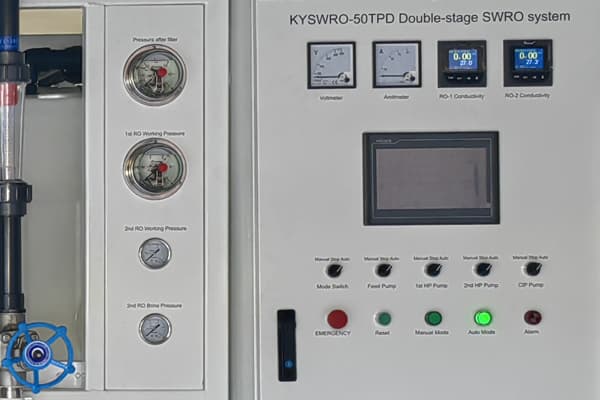
RO System Architecture: Arrangements consist of single-stage, multistage (for higher healing), and two-pass (for higher purity Elements: High-pressure pump (typically with VFDs, membrane vessels, RO membrane aspects (commonly polyamide), control system (SCADA/PLC) for tracking and automation.
Membrane layer Kinds: Choice relies on feed water. Unique products improve performance: Nanocomposites (carbon nanotubes, graphene oxide, MOFs). Not natural, CNT, Graphene, Mixed Matrix [Understanding 5, point I. Mixed Matrix Membranes (MMMs)], Biomimetic (aquaporins) , Polyimide/Graphene Oxide.
التحجيم: Design balances recuperation, feed quality, and business economics. Number of elements/stages is optimized. Corrosion-resistant products are essential for salt water. Modular designs provide versatility. Keeping track of pH, temperature level, healing prevents fouling/scaling.
How is the performance of industrial reverse osmosis systems?
Effective procedure and monitoring take full advantage of effectiveness and lifespan.
Critical Criteria: Stress (feed, permeate, focus), circulation rates, temperature, pH, inlet water quality (TDS, turbidity, SDI, ORP).
طرق التحكم: SCADA/PLC systems systematize monitoring and control, making it possible for computerized adjustments.
Functional Optimization: .
- Pretreatment: First defense versus fouling/scaling.
- Flux Upkeep: Flushing, backwashing, chemical cleaning. Saturating components aids.
- Stress Optimization: Least expensive effective pressure reduces power, compaction, fouling.
- Recovery Price Administration: Prevents excessive solute concentration.
- Energy Efficiency: VFDs, pressure optimization, ERDs decrease SEC.
- Membrane layer Cleansing: Structured methods with appropriate chemicals. Low pH cleaners commonly initial step.
- Feed Water Top Quality: Keeping regular high quality is fundamental.
Scaling and Fouling Control: Exact water analysis (e.g., CCPP) anticipates scaling. Appropriate antiscalant/biocide dosing is critical. Fouling-resistant membranes or style attributes like FR-RO assistance.
Technology and Automation: SCADA/PLC allow remote tracking, automation, and efficiency. Digital twins are discovered for optimization.
Future Study: ML for anticipating upkeep, anomaly discovery, dynamic optimization.Dynamic optimization for differing feed. Modeling crossbreed systems.
Financial Evaluation and Upkeep Routines
Business economics entail Life Cycle Expense (LCC) evaluation (CapEx and OpEx) and maintenance. LCA structures examine ecological and financial impacts.
- Capital Investment (CapEx): Initial costs for pumps, vessels, membranes, controls, civil jobs.
- Operational Expenditures (OpEx): Continuous expenses for energy, chemicals, labor, membrane replacement, maintenance.
Economic Metrics: NPV assesses success over life time. Levelized price of water contrasts modern technologie. Ecological externalities are increasingly consisted of.
Membrane Lifespan: Influenced by fouling, scaling, chemical attack (e.g., chlorine), physical damage. Replacement is a considerable OpEx.Cleaning vs. substitute is an economic choice.
Membrane Repair/Recycling: Study discovers techno-economic stability to minimize waste and prices. Reusing can substantially reduce costs (e.g., 60%) and environmental impact. More beneficial for brackish water membrane layers.”Minimum valuable life” indications guide choices.
Maintenance Regimens: Essential for avoiding failing and optimizing efficiency. Consists of keeping track of KPIs, pre-treatment, arranged cleansing. Soaking membrane layers helps.KPIs signal requirement for fixing.Details cleaning procedures utilize ideal chemicals.
Get The Solution Today!