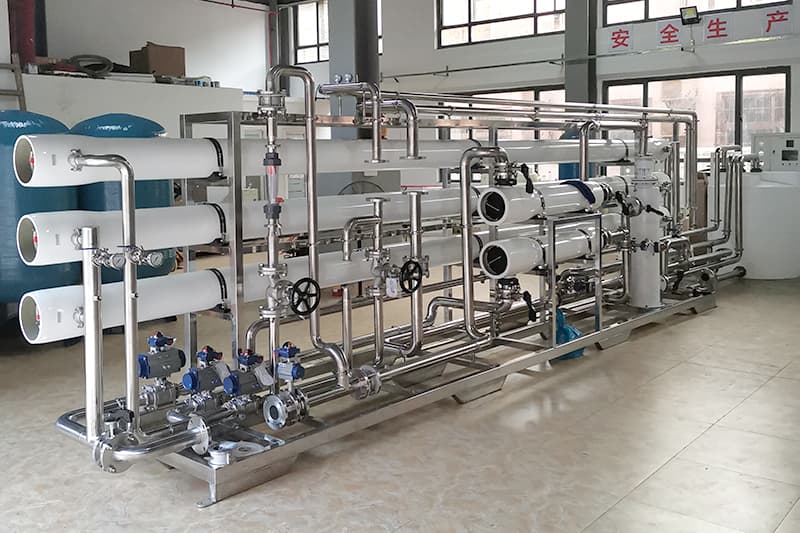
In the context of increasing attention to water resources today, ro water treatment machines have become one of the main equipment in households, industries, and water management fields. But when faced with the dazzling array of products on the market, how to understand their principles and make precise choices?
What is ro water treatment machine?
RO water treatment machine is a water purification system that uses deceptive membrane separation technology. It provides energy through a high-pressure pump, allowing the aqueous solution to pass through an extremely fine semi permeable membrane, effectively removing impurities such as dissolved salts and organic matter from the water;
Reverse osmosis (RO), also known as reverse osmosis, is a membrane separation manipulation driven by pressure difference! Its name comes from its working principle that contradicts the natural permeation process: under an external pressure higher than the osmotic pressure of the solution, the solvent (water) passes through the semi permeable membrane in reverse from the concentrated solution side to the dilute solution side, thereby achieving the separation of solvent and solute!
How does RO water treatment machine work?
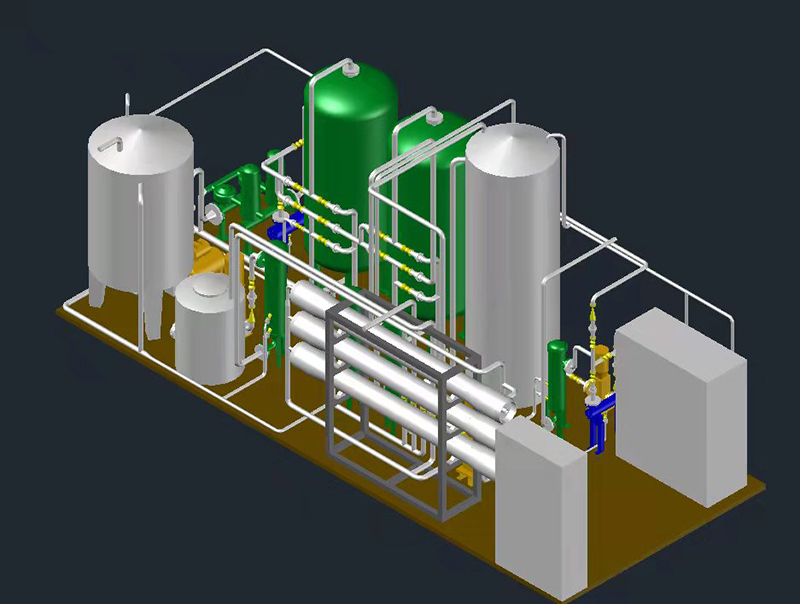
The operating mechanism of reverse osmosis ro water treatment machine involves a precise multi-stage filtration process; The general system includes three main parts: pre-processing unit, reverse osmosis host, and post-processing system!
The preprocessing system usually consists of quartz sand filters, activated carbon filters, and compact filters. Quartz sand filters mainly remove larger particles and impurities such as suspended solids and sediment from water! Activated carbon filters utilize their rich pore structure to adsorb residual chlorine in water, while softeners use ion exchange resins to reduce water hardness and prevent subsequent RO membrane fouling!
The reverse osmosis membrane is with a pore size of only 0.0001 micrometers (approximately one millionth of the diameter of a human hair), which can effectively trap small impurities such as bacteria and heavy metal ions; Under the external pressure provided by the high-pressure pump, water molecules are forced to pass through the RO membrane, and pollutants are concentrated and released!
Post processing preparation may include ion exchangers, EDI assemblies, or ultraviolet sterilization lamps to further purify water quality or regulate taste, ensuring that the effluent meets specific application needs.
What are the components of a RO water treatment machine?
A complete reverse osmosis system consists of multiple key components working together, mainly including:
- Pre treatment system : includes multi-media filters (such as quartz sand), activated carbon filters, and ensures that the incoming water meets the requirements of the RO membrane! -High pressure pump: provides stable and sufficient pressure for preparation (usually 6.5-8.0MPa for brackish water desalination and 8.5-10.0MPa for seawater desalination), and is the power source for reverse osmosis process;
- Reverse osmosis membrane module: Focus separation element, modern composite membrane desalination rate can reach over 99.5%.
- Membrane housing(pressure vessel): accommodates reverse osmosis membrane components and receives high-pressure operating environment;
- Edge and Control System: Integrating flow meters, conductivity meters, and PLC control systems to achieve automated operation and monitoring! -Post processing unit: configured as needed, such as adding ion exchange or EDI settings for ultra pure water systems!
How to choose RO water treatment machine based on water quality?
When choosing ro water treatment machine, the characteristics of the water source are the primary consideration! The significant differences in impurity identity and content among different water sources directly affect the setting configuration and pre-treatment needs!
The following table summarizes the characteristics of different water sources and the precautions for RO treatment:
| Water source type | TDS example category (ppm) | Main features | RO treatment precautions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Municipal tap water | 100-500 | capable of containing residual chlorine and relatively stable water quality | requires attention to residual chlorine content (should be ≤ 0.1mg/L) and equipped with activated carbon filtration |
| Groundwater | Variable, often high hardness | High ion content, low turbidity | Must be equipped with softening pretreatment to prevent calcium and magnesium scaling |
| Surface water (rivers, lakes) | generally low, but highly variable | turbidity, organic matter content can be high, seasonal fluctuations are obvious | need to deepen flocculation and pay attention to microbial confusion |
| Bitter and salty water | 1000-10000 | High salt content and high osmotic pressure | Special membranes for bitter and salty water need to be used, with high operating pressure |
| Seawater | >35000 | Extremely high salt content, high corrosiveness | Must use seawater desalination special membranes and high-pressure preparation |
After determining the water source, water quality testing should be conducted to identify examples of pollutants that need to be removed (such as heavy metals), and to select settings equipped with corresponding pre-treatment processes!
What is the impact of Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) on RO programming?
Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) is a key target for measuring the total concentration of all dissolved ions, salts, and organic matter in water, directly sensing the design pressure and operating costs of reverse osmosis.
The TDS value is positively correlated with the osmotic pressure of the raw water! Due to their high salt content, brackish water (TDS approximately 1000-10000 ppm) and seawater (TDS> 35000 ppm) require RO equipment to be equipped with higher pressure pumps and more pressure resistant membrane elements, which directly leads to increased equipment investment and energy consumption; The water production flux may decrease because the pressure required to drive water molecules through the membrane requires a higher osmotic pressure; High TDS inflow also requires higher desalination rate of the membrane to ensure that the water quality meets the standard;
Home users can use a TDS pen to quickly measure the TDS of raw water (if it is below 1000ppm)! If the TDS of the water source is too high or the composition is mixed, it is recommended to submit it to a specialized laboratory for testing to provide accurate basis for equipment selection.
Why is there such a big price difference for RO water treatment machines?
The price difference of reverse osmosis ro water treatment machine is mainly due to factors such as the quality of core components, processing scale, and customization needs!
The texture of membrane components is a key factor; The cost difference between high-quality composite membranes with a leading desalination rate of 99.5% and ordinary membranes is significant;
Both the field of management and the recycling rate are equally sensitive to price. Large industrial systems (with a water production capacity of several tons/hour or more) require more membrane components, stronger pumps, and more complex control systems, with much higher investment than household small-scale machines;
The quality of incoming water determines the complexity of the pretreatment system. High hardness or high suspended solids water sources require more comprehensive pretreatment (such as sand filtration, which sometimes even exceeds the investment of the host itself), but it is crucial to cherish the RO membrane and maintain stable system operation!
How to maintain a reverse osmosis water treatment machine?
Regular maintenance is the core to ensure the long-term stable operation of the reverse osmosis system and extend the membrane life.
Daily monitoring and recording are crucial! It is necessary to regularly inspect and record parameters such as pure water conductivity, pressure and flow rate at each point, and promptly investigate any abnormalities found.
RO membrane cleaning cannot be ignored. When the water production decreases by more than 10% or the desalination rate significantly decreases, chemical cleaning is required to remove membrane surface pollutants (such as calcium carbonate scale, metal oxides, biofilms, etc.);
Attention should also be paid to cherishing downtime during preparation; When not in use for a long time, precious liquid should be injected to prevent microbial growth and membrane drying and aging;
What are the main application of reverse osmosis technology?
The ability of reverse osmosis, with its efficient desalination and wide applicability , has played a key role in many fields!
In the field of stable drinking water, household RO water purifiers can effectively remove pathogenic microorganisms, pesticide residues, etc., providing pure water for direct drinking; In the field of industrial pure water preparation, pharmaceutical and other industries require ultrapure water for cleaning, formulation and production. Reverse osmosis is often combined with ion exchange, EDI and other technologies to prepare ultrapure water with a resistivity of up to 18 megaohms · cm!
Seawater desalination و تحلية المياه المالحة is an important way to solve water shortage in coastal areas and water islands! The treatment of boiler feedwater in industries such as petrochemicals also widely adopts RO technology to prevent scaling and corrosion, and improve thermal efficiency;
What we consider when choosing a RO water treatment machine?
Choosing suitable reverse osmosis ro water treatment machine requires a comprehensive evaluation of water production needs , water quality targets , and economy !
Clear understanding of the required amount of pure water per hour or day is fundamental; The specifications for household machines are 50-100 GPD (gallons per day), while for industrial settings, the number of membrane components needs to be calculated based on continuous production capacity requirements (such as a single 8-inch membrane producing approximately 0.5-1 ton/hour of water)!
The demand for effluent quality determines the technical approach. The desalination rate of drinking water should be ≥ 99.5%, and the TDS should be reduced to below 10ppm; Electronic grade ultrapure water can require secondary RO combined with precision control, which affects operating costs in terms of energy consumption and wastewater ratio. Therefore, low wastewater ratio equipment (such as 1:1) is preferred for energy conservation and environmental protection.
The level of brand after-sales service and intelligence (such as automatic flushing and remote monitoring) is also related to long-term usage and maintenance costs; Understanding the basic principles of reverse osmosis, its component composition, and its relationship with water source characteristics is the foundation for making smart investment decisions; Accurate selection and maintenance not only ensure water quality safety, but also improve compliance and extend the service life of the equipment;
Get The Solution Today!