The seawater desalination membrane is the core component of the Meerwasserentsalzungsanlage, and its service life directly affects the operating cost and stability of the entire system. Many users are concerned about how long a seawater desalination membrane can last? In fact, its service life is not fixed and unchanging, but is determined by multiple factors. This article will comprehensively analyze the key factors that affect the lifespan of seawater desalination membranes and provide practical solutions to extend their lifespan.
How long is the service life of seawater desalination membranes?
The service life of seawater desalination membranes is generally between 2-5 years , and high-quality membranes can reach more than 5 years under ideal conditions. For example, the Huitong SW8040LE-400 seawater desalination membrane can have a lifespan of several years with proper use and maintenance, while the typical lifespan of the Dow SW30HRLE-370/34i reverse osmosis membrane is 3-5 years. It is worth noting that some high-performance membranes, when combined with high-quality pretreatment systems, can even maintain longer stable performance. For example, the BFUF2800 series ultrafiltration membrane from Bifei has demonstrated a zero wire breakage operation record of up to 8 years in power plant applications.
What factors can shorten the lifespan of seawater desalination membranes?
Water quality
The quality of the incoming water is the primary factor affecting the lifespan of the membrane. The large amount of impurities, microorganisms, and particulate matter contained in seawater can accumulate on the membrane surface to form fouling, affecting the flux and performance of the membrane. High concentration hardness ions (calcium, magnesium) will form scale on the membrane surface, blocking the membrane pores; Organic substances such as humic acid, proteins, oils, etc. will adsorb onto the membrane surface, altering the surface properties of the membrane; Microorganisms and colloidal particles will adhere and aggregate on the surface of the membrane, forming biofilms, blocking membrane pores, and potentially corroding membrane materials.
Operating conditions
The operating pressure and flow rate have a significant impact on membrane life. Excessive operating pressure may lead to physical damage or premature aging of the membrane. Temperature is also a key factor – too high a temperature can accelerate the aging and hydrolysis of membrane materials, while too low a temperature can increase water viscosity and reduce membrane flux. Improper settings of inlet flow rate and recovery rate can exacerbate concentration polarization and increase the risk of membrane fouling.
Chemical factors
Residual chlorine and other oxidants can cause oxidative damage to reverse osmosis membranes, especially polyamide membranes that are highly sensitive to residual chlorine. PH values exceeding the appropriate range of the membrane may cause hydrolysis or chemical damage to the membrane. The continuous operation pH range of the Suez AE-400 seawater desalination membrane is 2-11, and exceeding this range can damage the membrane performance.
How does the quality of membrane materials affect their service life?
The quality of membrane materials is the basis for determining their service life. High quality membrane materials have better chemical and physical stability. The current mainstream seawater desalination membrane materials include two categories: cellulose acetate and polyamide. Polyamide membranes have high mechanical strength and chemical stability, but are sensitive to oxidants; However, the chemical stability of cellulose acetate membrane is relatively poor, and it is easily affected by acidity, alkalinity, and microorganisms.
Advanced manufacturing processes can also extend the service life of membranes. For example, reverse osmosis membranes prepared using new activation crosslinking technology and modified crosslinking technology have higher crosslinking degree and smaller free volume of polymer chains, enhancing the density and anti pollution performance of the desalination layer. The polyamide composite membrane technology used in the Suez AD-400 seawater desalination membrane enables it to maintain good filtration performance even under complex water quality conditions such as high salt concentration and pH changes.
Performance comparison of different types of seawater desalination membranes
| Membrane Type | Typical Service Life | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polyamide composite film | 3-5 years | High mechanical strength, good chemical stability | Sensitive to oxidants |
| Acetate cellulose membrane | 2-4 years | Good hydrophilicity, high retention rate for certain organic compounds | Poor chemical stability and temperature resistance |
| New modified membrane | Can last for more than 5 years | Strong anti pollution performance, high desalination rate | High cost |
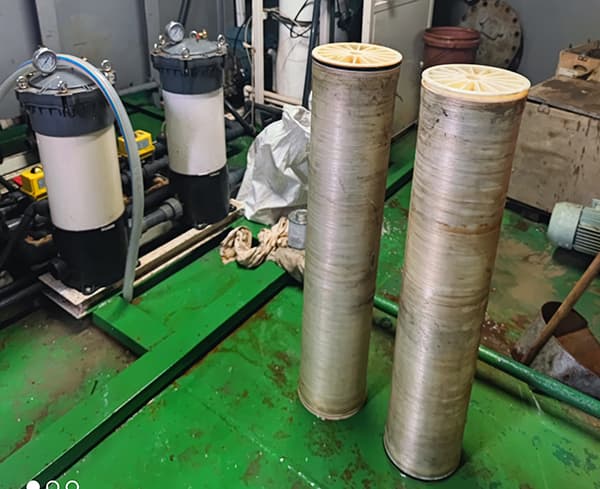

Does the quality of membrane material affect its service life?
Stress management
Appropriate operating pressure is the key to ensuring membrane performance. Excessive pressure can cause physical damage to the membrane, and long-term operation beyond the membrane’s rated pressure can cause deformation of the membrane structure, leading to an irreversible decrease in flux. For example, the Dow SW30HRLE-370/34i reverse osmosis membrane needs to be gradually depressurized to around 3bar during shutdown and rinsed with pre treated water to prevent membrane fouling.
Temperature control
The inlet water temperature directly affects the performance and lifespan of the membrane. The Suez AD-440 seawater desalination membrane performs best below 50 ℃, as temperature changes can affect water production and desalination rate. An increase in temperature will reduce the viscosity of water and increase the permeation rate of water molecules through the membrane, but excessive temperature will accelerate the aging of the membrane material. In low-temperature environments, it is necessary to adjust the water temperature through a preheating system or adjust the working pressure to compensate for the decrease in water production.
Optimization of traffic and recovery rate
The reasonable setting of inlet flow rate and recovery rate is crucial for membrane lifespan. Low flow rate will make it easier for impurities in water to deposit on the membrane surface; If the recovery rate is too high, it will exacerbate the concentration polarization phenomenon. According to the operating instructions provided by the membrane supplier, controlling appropriate operating parameters can significantly extend the service life of the membrane.
How to extend the lifespan of seawater desalination membranes?
Regular cleaning strateg
Regular cleaning is the key to maintaining membrane performance. The cleaning frequency and method should be determined based on the degree of membrane fouling and operating conditions. When performing chemical cleaning, it is necessary to choose appropriate cleaning agents and cleaning procedures – using inappropriate cleaning agents may cause damage to the membrane. For the Suez AE-400 seawater desalination membrane, the pH value during cleaning should be controlled within the range of 1.0-12.0.
The cleaning steps generally include: first rinse the system with clean water; Use a suitable cleaning agent (which may contain chelating agents such as EDTA or sodium hexametaphosphate) for cyclic cleaning; Remove the cleaning agent with clean water; Evaluate membrane performance; Repeat the cleaning steps if necessary.
Preprocessing system maintenance
Pre treatment is the first line of defense for protecting seawater desalination membranes. Appropriate pre-treatment equipment such as multi-media filters, activated carbon filters, and precision filters can effectively reduce pollutants in the influent and alleviate the burden on the membrane. Regular maintenance of the pre-treatment system is equally important, including backwashing of quartz sand filters and activated carbon filters, as well as regular replacement of filter media.
Ultrafiltration, as a pretreatment technique, can significantly extend the lifespan of reverse osmosis membranes. The BFUF2800 series ultrafiltration membrane from Bifei provides stable influent with SDI<3.0 for RO systems through high-quality pore size distribution and anti breakage design, extending the RO membrane replacement cycle from 2-3 years to 3-5 years.
Daily monitoring and maintenance
Regularly inspect all components and connection points of the membrane system, including membrane shells, pipelines, valves, and seals, to ensure no leakage, damage, or wear. Establishing complete maintenance records, including the operation and cleaning status of the membrane, can help monitor its service life and perform timely maintenance.
Appropriate maintenance measures should be taken when the equipment is not in use for a long time. For example, new reverse osmosis membranes are usually soaked in protective solution and stored in sealed plastic bags. Once opened, they should be used as soon as possible. When shutting down, it is necessary to rinse according to the correct procedure to prevent membrane fouling.
Schlussfolgerung
The service life of seawater desalination membranes is affected by various factors, generally up to 2-5 years, and high-quality membranes can even be longer under ideal conditions. In order to maximize the service life of the membrane, users should choose high-quality membrane materials, optimize operating parameters (especially pressure, temperature, and pH), implement effective pretreatment, and implement regular cleaning and maintenance plans. Through scientific operation management and maintenance strategies, not only can the service life of seawater desalination membranes be extended, but the economy and reliability of the entire seawater desalination system can also be improved.
Get The Solution Today!